U-Boot Variables
U-Boot uses environment variables to configure boot behavior, kernel parameters, and device settings. These variables are stored in persistent storage (eMMC, NAND, or SPI flash) and can be modified at runtime.
How to enter into u-boot mode
When you turn on the Mecha comet device it follows the boot-up process and present to you with the **Mechanix OS running GUI. but if you want to bring your device into u-boot console you need to follow several steps that are given bellow
- Connect your Mecha comet device to your host machine using USB to TTL Serial cable
- Open a terminal window to monitor the UART logs form the Mecha comet device.You can use tools such as CoolTerm or PuTTY or minicom (on Linux). With PuTTY and minicom you will get native console like feel. You will need to configure your serial port setting for your Board.
here is an example of that, i am using screen program to connect to device over serial with Baud Rate : 115200
-
when you press enter it will ask for your host machine authentication if you’re using with sudo.
-
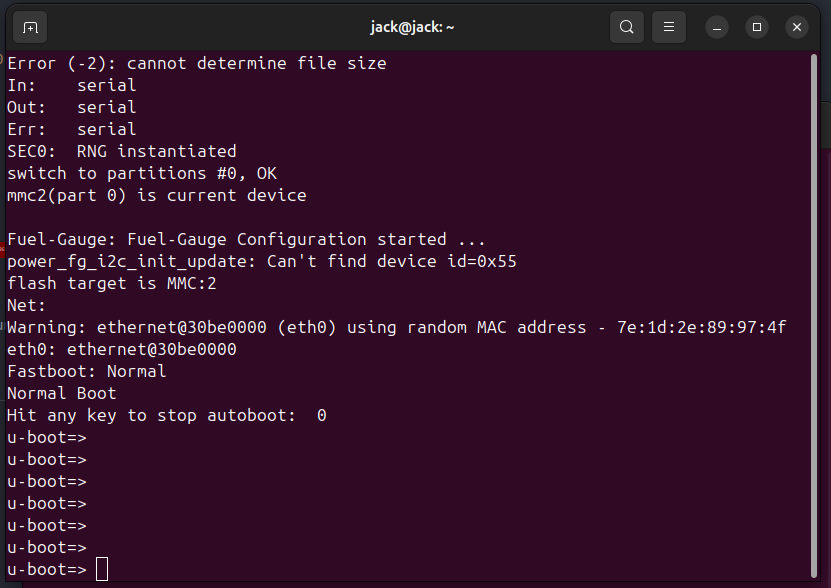
after that you can see logs flooding through the terminal you need to look for line
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 0 -
you need to press any key to enter into u-boot mode. if it’s too fast to read keep pressing the key till you obtain u-boot mode
Working with u-boot variables:
Checking Current Variables
To view all available U-Boot environment variables, use:
$ printenv
here is an example form Mecha comet device U-Boot environment variables
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
arch | arm |
board | mecha_comet |
board_name | Comet-m |
board_rev | Gen1 |
boot_targets | usb0 mmc1 mmc2 |
bootcmd | run sr_ir_v2_cmd;run distro_bootcmd;run bsp_bootcmd |
console | ttymxc1,115200 |
cpu | armv8 |
fdt_file | imx8mm-mecha-comet-m-gen1.dtb |
kernel_addr_r | 0x40400000 |
initrd_addr | 0x43800000 |
mmcroot | /dev/mmcblk2p2 rootwait rw |
soc | imx8m |
soc_type | imx8mm |
vendor | mecha |
To check a specific variable
$ printenv ${varible}
Example form Mecha comet
u-boot=> printenv console
console=ttymxc1,115200
u-boot=>printenv board_name
board_name=Comet-m
Commonly Used U-Boot Variables on Mecha Comet
| Variable | Purpose |
|---|---|
bootcmd | The main command executed at boot. It loads the kernel and boots the OS. |
bootargs | Kernel command-line parameters, passed to the Linux kernel. |
console | Defines the serial console device for debugging (e.g., ttyS0,115200). |
fdtfile | Specifies the device tree file to load. |
fdt_addr_r | Memory address where the device tree is loaded. |
kernel_addr_r | Load address for the Linux kernel in RAM. |
root | Specifies the root filesystem location. |
Modifying U-Boot Variables
Temporarily Changing a Variable (Does Not Persist After Reboot)
You can modify variables for the current session using:
$ setenv bootargs "console=ttyS0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rw"
To verify the change:
$ printenv bootargs
Permanently Saving Variables
To save changes so they persist after reboot:
$ saveenv
Example Boot Variables for Mecha Comet
$ setenv bootargs "console=ttyS0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk2p2 rw"
$ setenv bootcmd "run distro_bootcmd"
$ setenv fdtfile "imx8mm-mecha-comet-m-gen1.dtb"
$ saveenv
Explanation of Key Variables
bootcmd: Commands to load and boot the Linux kernel from eMMC.bootargs: Kernel parameters, such as the root filesystem and console settings.fdtfile: Specifies the correct device tree for Mecha Comet.
Restoring Default U-Boot Variables
If you need to reset everything to default settings:
$ env default -a
$ saveenv
Reboot the device after resetting:
$ reset
Conclusion
U-Boot variables control the boot process and can be customized for Mecha Comet to optimize boot time, enable debugging, and set up the correct kernel and root file-system

